Understanding market cycles and adapting your trading strategy accordingly is one of the most critical skills for long-term success in cryptocurrency trading. The strategies that work brilliantly in a bull market can lead to devastating losses in a bear market, and vice versa. This comprehensive guide will help you recognise different market conditions, understand their characteristics, and develop effective strategies for each phase of the market cycle.
Understanding Market Cycles: The Foundation
Cryptocurrency markets, like all financial markets, move in cycles. These cycles are driven by a combination of factors, including market sentiment, technological developments, regulatory news, macroeconomic conditions, and the natural psychology of fear and greed that governs human behaviour.
A complete market cycle typically consists of four distinct phases: accumulation, markup (bull market), distribution, and markdown (bear market). Each phase has unique characteristics, and recognising which phase you're in can dramatically improve your trading results.
Understanding that markets are cyclical helps you maintain perspective during both euphoric highs and fearful lows. No bull market lasts forever, and no bear market is permanent. This knowledge alone can prevent costly emotional decisions and help you position yourself advantageously for the next phase of the cycle.
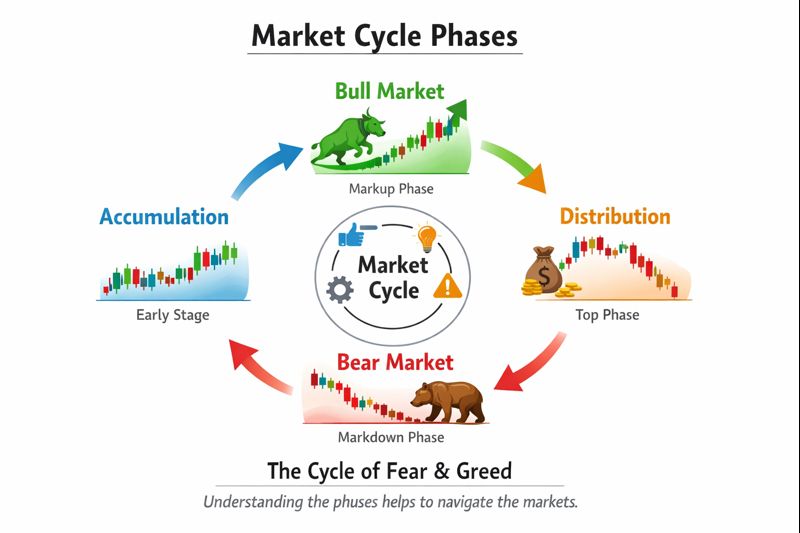
IMAGE SOURCE: Created by Author
What Is a Bull Market?
A bull market is a sustained period of rising prices characterised by optimism, investor confidence, and strong demand. In cryptocurrency markets, bull markets often feature dramatic price increases that can last for months or even years.
The defining characteristics of a bull market include consistently higher highs and higher lows in price action, strong trading volume on up days, positive market sentiment and media coverage, increased retail and institutional participation, new investors entering the market enthusiastically, and altcoins outperforming during later stages.
Bull markets in cryptocurrency are often more intense than in traditional markets. It's not uncommon to see major cryptocurrencies double or triple in value within months, while smaller altcoins can experience even more explosive growth. Bitcoin's rise from around $10,000 in September 2020 to nearly $69,000 in November 2021 exemplifies a powerful cryptocurrency bull market.
Psychologically, bull markets are characterised by optimism, greed, and sometimes euphoria. Fear of missing out becomes a dominant emotion, driving people to buy at increasingly higher prices. Social media and news coverage become overwhelmingly positive, and everyone seems to be making money.
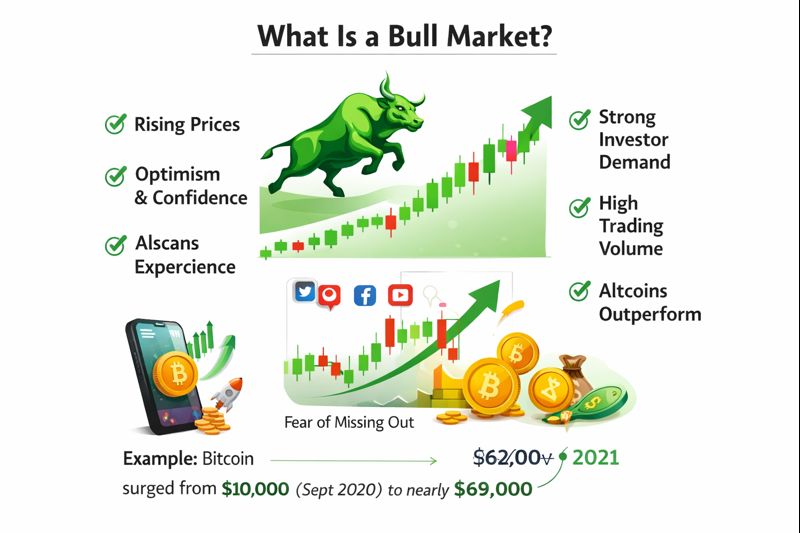
IMAGE SOURCE: Created by Author
What Is a Bear Market?
A bear market is a prolonged period of declining prices characterised by pessimism, fear, and a decline in investor confidence. Bear markets are often defined as a decline of 20% or more from recent highs, though in cryptocurrency, declines of 50-80% are not uncommon.
The characteristics of a bear market include consistently lower highs and lower lows, strong volume on down days, negative sentiment and media coverage, declining participation as investors leave the market, capitulation events where panic selling occurs, and reduced interest in altcoins as capital flows to safety or exits entirely.
Cryptocurrency bear markets can be fierce and lengthy. The bear market following the 2017 bull run saw Bitcoin decline by over 80% from its peak, and many altcoins fell by 90% or more. Recovery took several years, testing the patience and conviction of even experienced investors.
The psychological environment of bear markets is dominated by fear, despair, and apathy. Investors who were euphoric at the top become convinced that cryptocurrencies will never recover. Media coverage turns negative, and former enthusiasts abandon the space entirely. This maximum pessimism often marks the best buying opportunities, though recognising this in real-time is difficult.
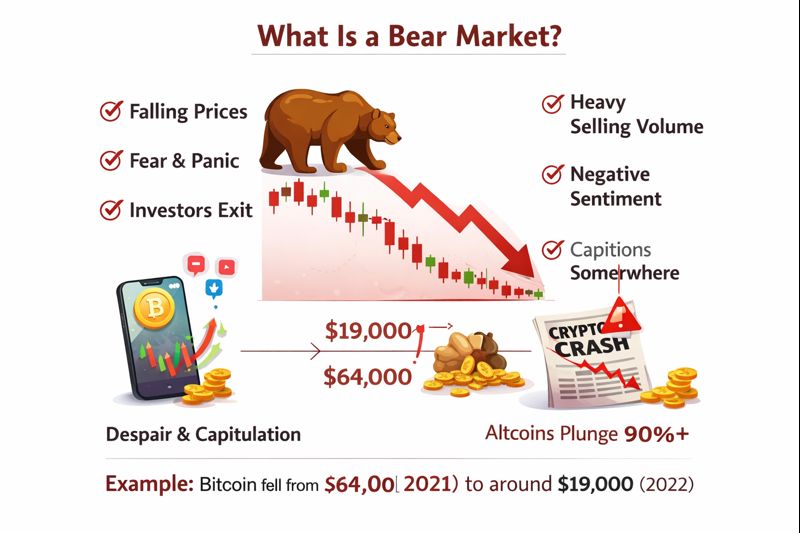
IMAGE SOURCE: Created by Author
Bull Market Trading Strategies
Trading successfully in a bull market requires strategies that capitalise on upward momentum while protecting profits from inevitable corrections.
Buy the Dip Strategy
It is one of the most effective approaches in bull markets. When prices experience temporary pullbacks during an overall uptrend, these dips represent buying opportunities. The key is distinguishing between a temporary dip and the beginning of a larger correction or trend reversal. Look for dips to established support levels, corrections of 10-20% from recent highs, and decreased volume during the pullback, indicating low selling pressure.
Momentum Trading
It involves buying cryptocurrencies that are showing strong upward momentum and riding the trend. In bull markets, assets that are outperforming tend to continue outperforming. Use technical indicators like moving averages to confirm momentum, enter on breakouts above resistance levels with strong volume, and set trailing stop losses to protect profits while allowing positions to run.
Sector Rotation
It becomes important as bull markets mature. Different sectors of the cryptocurrency market often take turns leading. Bitcoin typically leads at the start, followed by large-cap altcoins, then mid-cap altcoins, and finally small-cap and speculative projects during the euphoric final stages. Recognising this rotation allows you to move capital into sectors that are just beginning their run.
Position Scaling
It is crucial for managing risk in bull markets. Rather than going all-in at once, scale into positions gradually. This approach allows you to average your entry price and prevents the regret of missing further upside if you only bought a small amount.
Profit-Taking Strategy
It is essential because bull markets don't last forever. Establish clear profit targets and take partial profits at predetermined levels. A common approach is to take back your initial investment after a certain gain, then let the remaining position run with house money. Consider taking 25% profits at 2x, another 25% at 3x, and so on.
Bear Market Trading Strategies
Bear markets require a fundamentally different approach. The strategies that made you money in the bull market will likely lose you money if applied during a bear market.
Capital Preservation
Becomes the primary objective. In bear markets, not losing money is more important than making money. Holding cash or stablecoins is a valid strategy, as it preserves your purchasing power for when opportunities arise. Many of the best traders spend bear markets largely in cash, waiting patiently for the next cycle.
Short Selling and Futures
Offer opportunities to profit from declining prices. Using futures markets on LBank, you can open short positions that gain value as prices fall. However, shorting requires experience and careful risk management. The potential losses on short positions are theoretically unlimited if prices move against you, so use appropriate leverage and always employ stop losses.
Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA)
DCA is a powerful strategy for accumulating positions during bear markets. Rather than trying to catch the exact bottom, you invest fixed amounts at regular intervals regardless of price. This approach averages your entry price over time and removes emotion from the equation. The lower the prices go, the more cryptocurrency your fixed investment buys.
Focus on Quality Projects
Becomes even more important in bear markets. Weak projects often die during prolonged downturns, while strong projects with solid fundamentals, active development teams, and real use cases survive and thrive in the next bull market. Research thoroughly and invest in projects you believe will still exist in the next cycle.
Range Trading
Works well in bear markets where prices often move sideways for extended periods. Identify clear support and resistance levels and trade within that range. Buy near support, sell near resistance, and repeat. This strategy requires patience and discipline but can generate consistent returns in choppy markets.
Reduced Position Sizes
They are essential for managing risk. The uncertainty in bear markets is higher, so reduce your position sizes accordingly. Using only 25-50% of the position size you'd use in a bull market helps you survive the volatility and capital drawdowns.
Identifying Market Transitions: The Critical Moments
The most profitable and most dangerous moments in trading occur during market transitions. Recognising when a market is shifting from one phase to another can position you ahead of the crowd.
Bull to Bear Transitions
Often show warning signs before the full reversal occurs. Watch for decreasing volume on rallies, indicating weakening buying pressure, failure to make new highs while making lower lows, negative divergence on momentum indicators like RSI, increased volatility and larger price swings, and changing market sentiment with growing scepticism.
The distribution phase between bull and bear markets is when smart money exits positions while retail investors are still buying. Prices may appear to consolidate near highs, creating a false sense of security before the eventual decline.
Bear to Bull Transitions
They are harder to identify because they occur when sentiment is at its worst. Signs include decreasing volume on selloffs showing exhaustion of sellers, price stabilisation and formation of a base, positive divergence on momentum indicators, and small rallies that hold their gains instead of immediately reversing.
The accumulation phase between bear and bull markets is when smart money quietly builds positions while most people have given up. Prices may appear dead or boring, moving sideways for months, but this consolidation is building the foundation for the next bull run.
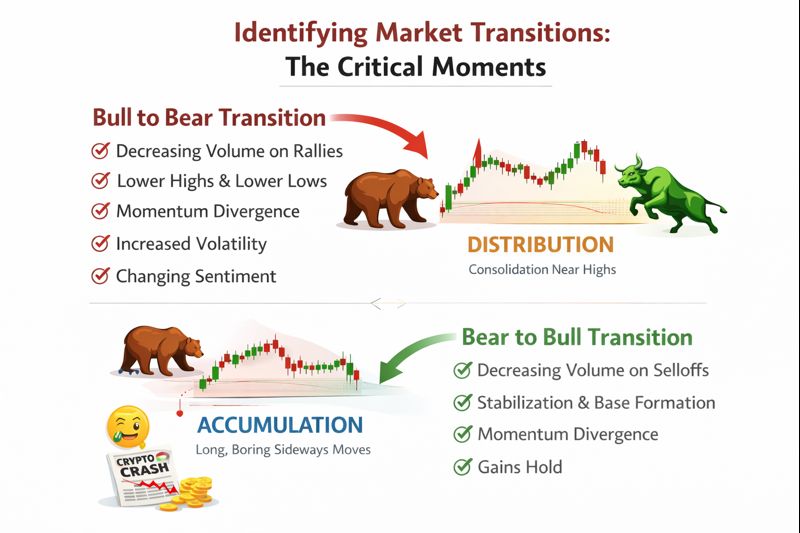
IMAGE SOURCE: Created by Author
Sideways Markets: The Forgotten Strategy
Between clear bull and bear markets, cryptocurrencies often trade in sideways ranges for extended periods. These consolidation phases require their own approach.
Range-Bound Trading
It is the primary strategy for sideways markets. Identify clear support and resistance boundaries and trade between them. Buy near the bottom of the range, sell near the top, and repeat. Use oscillators like RSI to identify overbought and oversold conditions within the range.
Breakout Preparation
It is important because ranges eventually break in one direction. As a range matures, prepare for the eventual breakout by watching for volume increases, tightening price action, and decreasing volatility preceding a major move. Position yourself to capitalise on the breakout while protecting against false breaks.
Reduced Trading Activity
Often makes sense in sideways markets. If clear opportunities aren't present, preserving capital and waiting for better conditions is perfectly acceptable. Not every market condition requires active trading.
Psychological Challenges in Different Markets
Each market condition presents unique psychological challenges that can derail even technically sound strategies.
In bull markets, the primary psychological trap is greed. As prices rise and everyone around you seems to be profiting, the temptation to abandon risk management and chase ever-higher prices becomes overwhelming. FOMO drives irrational decisions like buying at resistance levels or holding positions without taking profits. Combat this by sticking to your predetermined profit targets and remembering that you can't catch every move.
Overconfidence develops during bull markets as winning trades accumulate. Traders begin to feel invincible and take increasingly larger risks or abandon their proven strategies. This overconfidence often leads to giving back profits when the market turns.
In bear markets, fear and despair dominate. Watching your portfolio shrink day after day tests your emotional resilience. The temptation to capitulate and sell everything at the bottom is strongest when it would be most costly. Many traders also become paralysed by fear, unable to act on good opportunities because they're traumatised by previous losses.
Boredom becomes a challenge in sideways markets. When prices aren't moving dramatically, traders often force trades out of boredom, leading to unnecessary losses. Learning to be comfortable with inactivity is a crucial skill.
Risk Management Across Market Cycles
Effective risk management must adapt to market conditions while maintaining core principles.
In bull markets, you can afford to be more aggressive with position sizing since the trend is in your favour. However, you should still never risk more than you can afford to lose on any single trade. Use wider stop losses to avoid getting shaken out of winning positions by normal volatility, but always use stops. Increase your portfolio's risk exposure but maintain some cash reserves for opportunities and to take profits.
In bear markets, become more conservative by reducing position sizes significantly, using tighter stop losses since downtrends can accelerate quickly, and holding larger cash positions to preserve capital and provide dry powder for opportunities. The goal is survival and capital preservation, not maximising returns.
Volatility management is crucial across all cycles. Use appropriate leverage for the current market conditions, with higher leverage only in stable, trending markets. In highly volatile or uncertain markets, reduce or eliminate leverage entirely.
Tools and Indicators for Identifying Market Conditions
Several technical tools can help you identify which market condition you're in and when transitions might be occurring.
Moving Averages
MA are simple but effective. Price above the 200-day moving average generally indicates a bull market, while price below suggests a bear market. The relationship between shorter and longer moving averages also provides insights. A golden cross, when the 50-day moving average crosses above the 200-day, is a bullish signal, while a death cross, the opposite, is bearish.
Market Structure Analysis
Involves examining the pattern of highs and lows. Higher highs and higher lows confirm uptrends, while lower highs and lower lows confirm downtrends. A break in market structure, when an uptrend makes a lower low or a downtrend makes a higher high, often signals a potential reversal.
Volume Analysis
Provides confirmation. Increasing volume in the direction of the trend confirms its strength. Decreasing volume suggests the trend is weakening and may reverse.
Sentiment Indicators
Measure market psychology. Extreme greed often marks bull market tops, while extreme fear marks bear market bottoms. The Fear and Greed Index is a popular tool for gauging market sentiment.
Adapting Your Strategy: A Practical Framework
Successful traders don't use the same strategy in all market conditions. Here's a framework for adapting your approach.
Assessment Phase begins with regularly evaluating current market conditions using multiple timeframes. Look at daily, weekly, and monthly charts to understand both short-term action and longer-term trends. Identify which phase of the cycle you believe the market is in.
Strategy Selection follows assessment. Choose strategies appropriate for the identified market condition. In bull markets, focus on buying dips and momentum trading. In bear markets, emphasise capital preservation and selective short selling or DCA. In sideways markets, employ range trading and patience.
Position Sizing Adjustment changes based on confidence and market conditions. Increase size in favourable conditions with strong setups and reduce size in unfavourable conditions or lower-confidence trades.
Regular Review ensures your approach remains relevant. Markets evolve, and what worked last month may not work this month. Review your performance weekly or monthly and adjust as needed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Understanding what not to do is often as important as knowing what to do.
- Fighting the Trend is one of the most expensive mistakes. Trying to short a strong bull market or buy dips in a strong bear market typically results in losses. The trend is your friend until it's clearly over.
- Refusing to Adapt keeps you stuck in strategies that no longer work. Bull market strategies applied in bear markets lose money. Be flexible and willing to change your approach when conditions change.
- Emotional Decision Making overrides analysis during extremes. Making decisions based on fear or greed rather than analysis leads to buying tops and selling bottoms.
- Over-leveraging in any market condition amplifies losses when you're wrong. Use leverage cautiously and understand that it can destroy accounts quickly in volatile markets.
Final Thoughts About Crypto Market Cycles
Mastering the ability to identify market conditions and adapt your trading strategy accordingly is one of the most valuable skills you can develop. Bull markets, bear markets, and sideways markets each require different approaches, different risk management, and different psychological preparation.
The key to long-term success on LBank's trading platform isn't finding the one perfect strategy—it's developing the flexibility to employ the right strategy for the current market condition. This means being aggressive when conditions warrant it, defensive when necessary, and patient when appropriate.
Remember that market cycles are inevitable. Bull markets always end, bear markets always recover, and sideways markets always break out eventually. By understanding these cycles and adapting your approach to each phase, you position yourself not just to survive but to thrive across complete market cycles.
The most successful traders aren't those who make the most in bull markets—they're those who preserve capital in bear markets and position themselves advantageously for the next cycle. With the knowledge and strategies outlined in this guide, you're now equipped to navigate any market condition with confidence and adaptability.




